网站免费源代码,设计都有什么设计,网站推广软件有哪些,网站优化推广seo概述 介绍
ES 是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文搜索引擎#xff0c;是整个Elastic Stack技术栈的核心。它可以近乎实时的存储#xff0c;检索数据#xff1b;本身扩展性很好#xff0c;可以扩展到上百台服务器#xff0c;处理PB级别的数据。ElasticSearch的底层是开源库Lu…
概述 介绍
ES 是一个开源的高扩展的分布式全文搜索引擎是整个Elastic Stack技术栈的核心。它可以近乎实时的存储检索数据本身扩展性很好可以扩展到上百台服务器处理PB级别的数据。ElasticSearch的底层是开源库Lucene但是你没办法直接用Lucene必须自己写代码去调用它的接口Elastic是Lucene的封装提供了REST API的操作接口开箱即用。天然的跨平台。ElasticSearch是目前全文检索引擎的首选它可以快速的存储搜索和分析海量的数据维基百科GitHubStack Overflow都采用了ElasticSearch。 用途
- 搜索的数据对象是大量的非结构化的文本数据。
- 文件记录达到数十万或数百万个甚至更多。
- 支持大量基于交互式文本的查询。
- 需求非常灵活的全文搜索查询。
- 对高度相关的搜索结果的有特殊需求但是没有可用的关系数据库可以满足。
- 对不同记录类型非文本数据操作或安全事务处理的需求相对较少的情况。基本概念 Mysql擅长事务类型操作可以确保数据的安全和一致性Elasticsearch擅长海量数据的搜索、分析、计算MySQLElasticsearch说明TableIndex索引(index)就是文档的集合类似数据库的表(table)RowDocument文档Document就是一条条的数据类似数据库中的行Row文档都是JSON格式ColumnField字段Field就是JSON文档中的字段类似数据库中的列ColumnSchemaMappingMapping映射是索引中文档的约束例如字段类型约束。类似数据库的表结构SchemaSQLDSLDSL是elasticsearch提供的JSON风格的请求语句用来操作elasticsearch实现CRUD 索引
索引indices在这儿很容易和MySQL数据库中的索引产生混淆其实是和MySQL数据库中的Databases数据库的概念是一致的。
类型
类型(Type),对应的其实就是数据库中的 Table(数据表)类型是模拟mysql中的table概念一个索引库下可以有不同类型的索引比如商品索引订单索引其数据格式不同。
文档
文档(Document),对应的就是具体数据行(Row)。
字段
字段(field)相对于数据表中的列也就是文档中的属性。
倒排索引
Elasticsearch是通过Lucene的倒排索引技术实现比关系型数据库更快的过滤。特别是它对多条件的过滤支持非常好。
优点 根据词条搜索、模糊搜索时速度非常快 缺点 只能给词条创建索引而不是字段无法根据字段做排序 相关安装 Docker es安装
docker pull elasticsearch:7.4.2mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/config
mkdir -p /mydata/elasticsearch/data
echo http.host : 0.0.0.0 /mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.ymldocker run --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e ES_JAVA_OPTS-Xms64m -Xmx128m -v /mydata/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml -v /mydata/elasticsearch/data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data -v /mydata/elasticsearch/plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins -d elasticsearch:7.4.2# Elasticsearch Configuration
#
# NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings.
# Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you
# understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences.
#
# The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists
# the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster.
#
# Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options:
# https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html
#
# ---------------------------------- Cluster -----------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for your cluster:
#
cluster.name: my-application
#
# ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------
#
# Use a descriptive name for the node:
#
#node.name: node-1
#
# Add custom attributes to the node:
#
#node.attr.rack: r1
#
# ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------
#
# Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma):
#
#path.data: /path/to/data
#
# Path to log files:
#
#path.logs: /path/to/logs
#
# ----------------------------------- Memory -----------------------------------
#
# Lock the memory on startup:
#
#bootstrap.memory_lock: true
#
# Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available
# on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this
# limit.
#
# Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory.
#
# ---------------------------------- Network -----------------------------------
#
# By default Elasticsearch is only accessible on localhost. Set a different
# address here to expose this node on the network:
#
network.host: 0.0.0.0
#
# By default Elasticsearch listens for HTTP traffic on the first free port it
# finds starting at 9200. Set a specific HTTP port here:
#
http.port: 9200
#
# For more information, consult the network module documentation.
#
# --------------------------------- Discovery ----------------------------------
#
# Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when this node is started:
# The default list of hosts is [127.0.0.1, [::1]]
#
#discovery.seed_hosts: [host1, host2]
#
# Bootstrap the cluster using an initial set of master-eligible nodes:
#
#cluster.initial_master_nodes: [node-1]
#
# For more information, consult the discovery and cluster formation module documentation.
#
# ---------------------------------- Various -----------------------------------
#
# Allow wildcard deletion of indices:
#
#action.destructive_requires_name: false#true将启用X-Pack安全功能并默认禁止root用户访问
#xpack.security.enabled: false
#
xpack.security.enabled: falsediscovery.type: single-nodechmod -R 777 /mydata/elasticsearch/默认情况下不能root启动es docker kibana安装
docker pull kibana:7.4.2docker run --name kibana -e -p 5601:5601 -d kibana:7.4.2server.name: kibana
server.host: 0.0.0.0
elasticsearch.hosts: [ http://192.168.56.10:9200 ]
xpack.monitoring.ui.container.elasticsearch.enabled: trueES入门 _cat
_cat接口说明GET /_cat/nodes查看所有节点GET /_cat/health查看ES健康状况GET /_cat/master查看主节点GET /_cat/indices查看所有索引信息 字段名含义说明healthgreen(集群完整) yellow(单点正常、集群不完整) red(单点不正常)status是否能使用index索引名uuid索引统一编号pri主节点几个rep从节点几个docs.count文档数docs.deleted文档被删了多少store.size整体占空间大小pri.store.size主节点占 索引操作 创建索引
PUT http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引名
分片在ES中一个索引通常会被分解成多个部分这些部分就是分片。每个分片都是一个完整的Lucene索引可以独立地进行搜索和写入操作。通过将数据分布在多个分片上ES可以实现数据的并行处理提高系统的吞吐量和性能。每个分片可以独立地存储和处理一部分数据这样就能够有效地利用集群中的多个节点实现数据的分布式存储和处理。副本副本是分片的复制品它的存在主要是为了提高系统的容错性和可用性。每个分片可以有多个副本副本和原始分片之间保持数据的一致性。当某个节点故障或者网络发生故障时系统可以自动将副本升级为主分片确保数据的可用性和一致性。同时副本也可以处理查询请求分担主分片的查询压力。 查询索引
GET http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引名
{bobo: {aliases: {},mappings: {},settings: {index: {creation_date: 1702564134116,number_of_shards: 3,number_of_replicas: 2,uuid: VpSOVO9aR5OBPYtdvqgT8Q,version: {created: 7040299},provided_name: bobo}}}
}查询所有索引 http://192.168.56.10:9200/* 删除索引
DELETE http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引名 文档操作 创建文档
POST http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引/typess类型/22id POST方式如果id不写会自动生成id存在的情况下是更新POST和PUT方法PUT http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引/typess类型/22id PUT方式id必须填写
提交方式描述PUT提交的id如果不存在就是新增操作如果存在就是更新操作id不能为空POST如果不提供id会自动生成一个id,如果id存在就更新如果id不存在就新增 查看文档
GET http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引/typess类型/mAzcaIwBAOzWskCU9S7Nid
字段含义_index索引名称_type类型名称_id记录id_version版本号_seq_no并发控制字段每次更新都会1用来实现乐观锁_primary_term同上主分片重新分配如重启就会发生变化found找到结果_source真正的数据内容
乐观锁 更新文档
除了有无id来更新数据也可以使用另一种方式更新数据POST http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引/typess类型/mAzcaIwBAOzWskCU9S7Nid/_update如果更新的数据和文档中的数据是一样的那么POST方式提交是不会有任何操作的
{doc: {name: 王五,sex: 13,adds: 中国东部}
}删除文档
DELETE http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引/typess类型/1aad11idDELETE http://192.168.56.10:9200/bobo索引 删除整个索引 _bulk批量操作 POST /_bulk
{delete:{_index:website,_type:blog,_id:123}}{create:{_index:website,_type:blog,_id:123}}
{title:My first bolg post ...}{index:{_index:website,_type:blog}}
{title:My second blog post ...}{update:{_index:website,_type:blog,_id:123}}
{doc:{title:My updated blog post ...}}#! Deprecation: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
{took : 242,errors : false,items : [{delete : {_index : website,_type : blog,_id : 123,_version : 1,result : not_found,_shards : {total : 2,successful : 1,failed : 0},_seq_no : 0,_primary_term : 1,status : 404}},{create : {_index : website,_type : blog,_id : 123,_version : 2,result : created,_shards : {total : 2,successful : 1,failed : 0},_seq_no : 1,_primary_term : 1,status : 201}},{index : {_index : website,_type : blog,_id : mQwDaYwBAOzWskCUVy4x,_version : 1,result : created,_shards : {total : 2,successful : 1,failed : 0},_seq_no : 2,_primary_term : 1,status : 201}},{update : {_index : website,_type : blog,_id : 123,_version : 3,result : updated,_shards : {total : 2,successful : 1,failed : 0},_seq_no : 3,_primary_term : 1,status : 200}}]
}进阶 es的检索方式
在ElasticSearch中支持两种检索方式
通过使用REST request URL 发送检索参数(uri检索参数)通过使用 REST request body 来发送检索参数 (uri请求体)
第一种方式
POST /bank/account/_search?/q*sortaccount_number:desc
GEt /bank/account/_search?/q*sortaccount_number:desc//不写类型会查询索引 POST /bank/_search?sortaccount_number:desc GET /bank/_search?sortaccount_number:desc
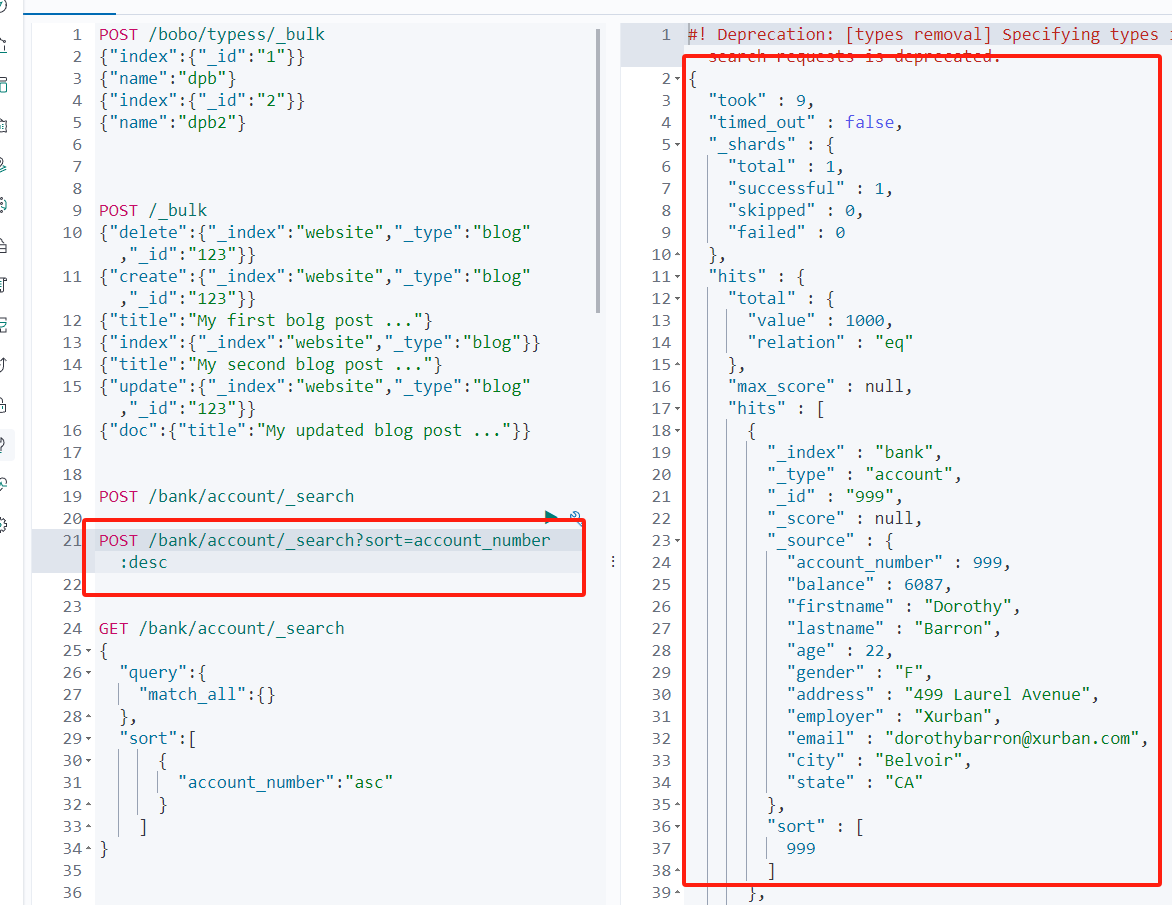| 信息 | 描述 |
| --- | --- |
| took | ElasticSearch执行搜索的时间(毫秒) |
| time_out | 搜索是否超时 |
| _shards | 有多少个分片被搜索了统计成功/失败的搜索分片 |
| hits | 搜索结果 |
| hits.total | 搜索结果统计 |
| hits.hits | 实际的搜索结果数组(默认为前10条文档) |
| sort | 结果的排序key没有就按照score排序 |
| score和max_score | 相关性得分和最高分(全文检索使用) |a nameuELY3/a
### 第二种方式
**match_all**:获取所有数据
json
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{match_all:{}},sort:[{account_number:asc}]
}Query DSL match
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{match:{account_number:20}}
}//模糊查询有分词功能分为Kings词和Place词查询出address包含这两个词的文档
//_score为相关计算分数也就是匹配度
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{match:{address:Kings Place}}
}match_phrase
不进行分词的检索短语匹配
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{match_phrase:{address:Kings Place}}
}multi_match
多字段匹配
//查询出state或者address中包含 NH Kings的记录
//有做分词
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{multi_match:{query:NH Kings,fields:[address,state]}}
}bool复合查询
组合查询bool把各种其它查询通过 must与、must_not非、should或的方式进行组合
//must必须是must_not必须不是
//必须age40且必须不是stateUT
GET /bank/account/_search
{query: {bool: {must: [{match: {age: 40}}],must_not: [{match: {state: UT}}]}}
} //address659 Highland Boulevard或state UT
GET /bank/account/_search
{query: {bool: {should: [{match_phrase: {address : 659 Highland Boulevard}},{match: {state : UT}}]}}
}filter[结果过滤]
//查address含有Pierrepont或Place会Pierrepont Place且state不为UT结果取age为20x35
GET /bank/account/_search
{query: {bool: {must: [{match: {address: Pierrepont Place}}],must_not: [{match: {state: UT}}],filter:{range:{age:{gte: 20,lte: 35}}}}}
}term
非text字段的精确匹配
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{term:{age : 28}}
}检索关键字描述term非text使用match在text中我们实现全文检索-分词match keyword在属性字段后加.keyword 实现精确查询-不分词match_phrase短语查询不分词模糊查询
GET /bank/account/_search
{query:{match:{city.keyword : Bellfountain}}
}聚合(aggregations)
聚合可以让我们极其方便的实现对数据的统计、分析。例如
什么品牌的手机最受欢迎这些手机的平均价格、最高价格、最低价格这些手机每月的销售情况如何 概念
Elasticsearch中的聚合包含多种类型最常用的两种一个叫 桶一个叫 度量。
桶
桶的作用是按照某种方式对数据进行分组每一组数据在ES中称为一个 桶例如我们根据国籍对人划分可以得到 中国桶、英国桶日本桶……或者我们按照年龄段对人进行划分0-10,10-20等。Elasticsearch中提供的划分桶的方式有很多
Date Histogram Aggregation根据日期阶梯分组例如给定阶梯为周会自动每周分为一组Histogram Aggregation根据数值阶梯分组与日期类似Terms Aggregation根据词条内容分组词条内容完全匹配的为一组Range Aggregation数值和日期的范围分组指定开始和结束然后按段分组……
bucket aggregations 只负责对数据进行分组并不进行计算因此往往bucket中往往会嵌套另一种聚合metrics aggregations即度量。
度量
度量分组完成以后我们一般会对组中的数据进行聚合运算例如求平均值、最大、最小、求和等这些在ES中称为 度量。比较常用的一些度量聚合方式
Avg Aggregation求平均值Max Aggregation求最大值Min Aggregation求最小值Percentiles Aggregation求百分比Stats Aggregation同时返回avg、max、min、sum、count等Sum Aggregation求和Top hits Aggregation求前几Value Count Aggregation求总数…… 实例 搜索address中包含mill的所有人的年龄分布以及平均年龄 //
GET /bank/account/_search
{
query: {match: {address: mill}
},
aggs: {//ageAgg为定义的变量名ageAggs: {//terms为内容分组terms: {//对那个字段进行分组age//分几组field: age,size: 10}},ageAvgs: {//对哪个字段进行平均值计算avg: {field: age}}
},
//查询的结果不显示
size: 0
}请求这些年龄段的这些人的平均薪资 GET /bank/account/_search
{
query: {match_all:{}
},
aggs: {balanceAvgs: {avg: {field: balance}}
},
size: 0
}查出所有年龄分布并且这些年龄段中M的平均薪资和F的平均薪资以及这个年龄段的总体平均薪资 GET /bank/account/_search
{
query: {match_all: {}
},
aggs: {ageAgg: {terms: {field: age,size: 50},aggs: {genderAgg: {terms: {field: gender.keyword,size: 10},aggs: {balanceAvg: {avg: {field: balance}}}},ageBalanceAvg: {avg: {field: balance}}}}
},
size: 0
}映射配置(_mapping) ElasticSearch7-去掉type概念
关系型数据库中两个数据表示是独立的即使他们里面有相同名称的列也不影响使用但ES中不是这样的。elasticsearch是基于Lucene开发的搜索引擎而ES中不同type下名称相同的filed最终在Lucene中的处理方式是一样的。两个不同type下的两个user_name在ES同一个索引下其实被认为是同一个filed你必须在两个不同的type中定义相同的filed映射。否则不同type中的相同字段名称就会在处理中出现冲突的情况导致Lucene处理效率下降。去掉type就是为了提高ES处理数据的效率。Elasticsearch 7.xURL中的type参数为可选。比如索引一个文档不再要求提供文档类型。Elasticsearch 8.x不再支持URL中的type参数。解决将索引从多类型迁移到单类型每种类型文档一个独立索引 创建映射字段
PUT /bank1/_mapping
{properties: {pid: {type: long,index: true,store: true,analyzer: ik_smart}}
}字段名类似于列名properties下可以指定许多字段。每个字段可以有很多属性。例如 type类型可以是text、long、short、date、integer、object等 index是否索引默认为true store是否存储默认为false analyzer分词器这里使用ik分词器ik_max_word或者ik_smart 新增映射字段 如果我们创建完成索引的映射关系后又要添加新的字段的映射这时怎么办第一个就是先删除索引然后调整后再新建索引映射还有一个方式就在已有的基础上新增。 更新映射
对于存在的映射字段我们不能更新更新必须创建新的索引进行数据迁移。 数据迁移
先创建出正确的索引然后使用如下的方式来进行数据的迁移
POST_reindex [固定写法]
{source:{index:twitter},dest:{index:new_twitter}
}老的数据有type的情况
POST _reindex
{source: {index: product//type: },dest: {index: mall-product}
}案例新创建了索引并指定了映射属性 分词 安装ik分词器
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik 下载对应的版本然后解压缩到plugins目录中然后检查是否安装成功进入容器 通过如下命令来检测检查下载的文件是否完整如果不完整就重新下载。插件安装OK后我们重新启动ElasticSearch服务 ik分词
ik_smart分词
# 通过ik分词器来分词
POST /_analyze
{analyzer: ik_smart,text: 我是中国人我热爱我的祖国
}ik_max_word
POST /_analyze
{analyzer: ik_max_word,text: 我是中国人我热爱我的祖国
}java ES整合
package com.example.elasticsearch.config;import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClientBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;/*** author guanglin.ma* date 2023-12-16 22:52*/
Configuration
public class MallElasticSearchConfiguration {public static final RequestOptions COMMON_OPTIONS;static {RequestOptions.Builder builde RequestOptions.DEFAULT.toBuilder();
// builde.addHeader(Authorization, Bearer TOKEN);
// builde.setHttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory(
// new HttpAsyncResponseConsumerFactory.
// HeapBufferedResponseConsumerFactory(30 * 1024 * 1024 * 1024));COMMON_OPTIONS builde.build();}Beanpublic RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient() {RestClientBuilder builder RestClient.builder(new HttpHost(192.168.56.10, 9200, http));RestHighLevelClient client new RestHighLevelClient(builder);return client;}
}dependencygroupIdorg.elasticsearch.client/groupIdartifactIdelasticsearch-rest-high-level-client/artifactIdversion7.4.2/version
/dependencypackage com.example.elasticsearch;import com.example.elasticsearch.config.MallElasticSearchConfiguration;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.rest.RestStatus;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.AggregationBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.AggregationBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.aggregations.metrics.avg.AvgAggregationBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.io.IOException;SpringBootTest
class ElasticsearchApplicationTests {Autowiredprivate RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;Testvoid contextLoads() {System.out.println(------ restHighLevelClient);}/*** 测试保存文档*/Testvoid saveIndex() throws Exception {IndexRequest indexRequest new IndexRequest(system);indexRequest.id(1);// indexRequest.source(name,bobokaoya,age,18,gender,男);User user new User();user.setName(bobo);user.setAge(22);user.setGender(男);// 用Jackson中的对象转json数据ObjectMapper objectMapper new ObjectMapper();String json objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user);indexRequest.source(json, XContentType.JSON);// 执行操作IndexResponse index restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 提取有用的返回信息System.out.println(index);}class User {private String name;private Integer age;private String gender;public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name name;}public Integer getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(Integer age) {this.age age;}public String getGender() {return gender;}public void setGender(String gender) {this.gender gender;}}//检索出所有的bank索引的所有文档Testvoid searchIndexAll() throws IOException {// 1.创建一个 SearchRequest 对象SearchRequest searchRequest new SearchRequest();searchRequest.indices(bank); // 设置我们要检索的数据对应的索引库SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder new SearchSourceBuilder();/*sourceBuilder.query();sourceBuilder.from();sourceBuilder.size();sourceBuilder.aggregation();*/searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);// 2.如何执行检索操作SearchResponse response restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 3.获取检索后的响应对象我们需要解析出我们关心的数据System.out.println(ElasticSearch检索的信息 response);}// 根据address全文检索Testvoid searchIndexByAddress() throws IOException {// 1.创建一个 SearchRequest 对象SearchRequest searchRequest new SearchRequest();searchRequest.indices(bank); // 设置我们要检索的数据对应的索引库SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder new SearchSourceBuilder();// 查询出bank下 address 中包含 mill的记录sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery(address, mill));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);// System.out.println(searchRequest);// 2.如何执行检索操作SearchResponse response restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 3.获取检索后的响应对象我们需要解析出我们关心的数据System.out.println(ElasticSearch检索的信息 response);}// 嵌套的聚合操作检索出bank下的年龄分布和每个年龄段的平均薪资Testvoid searchIndexAggregation() throws IOException {// 1.创建一个 SearchRequest 对象SearchRequest searchRequest new SearchRequest();searchRequest.indices(bank); // 设置我们要检索的数据对应的索引库SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder new SearchSourceBuilder();// 查询出bank下 所有的文档sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());// 聚合 aggregation// 聚合bank下年龄的分布和每个年龄段的平均薪资AggregationBuilder aggregationBuiler AggregationBuilders.terms(ageAgg).field(age).size(10);// 嵌套聚合aggregationBuiler.subAggregation(AggregationBuilders.avg(balanceAvg).field(balance));sourceBuilder.aggregation(aggregationBuiler);sourceBuilder.size(0); // 聚合的时候就不用显示满足条件的文档内容了searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);System.out.println(sourceBuilder);// 2.如何执行检索操作SearchResponse response restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 3.获取检索后的响应对象我们需要解析出我们关心的数据System.out.println(response);}//并行的聚合操作查询出bank下年龄段的分布和总的平均薪资Testvoid searchIndexAggregation1() throws IOException {// 1.创建一个 SearchRequest 对象SearchRequest searchRequest new SearchRequest();searchRequest.indices(bank); // 设置我们要检索的数据对应的索引库SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder new SearchSourceBuilder();// 查询出bank下 所有的文档sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());// 聚合 aggregation// 聚合bank下年龄的分布和平均薪资AggregationBuilder aggregationBuiler AggregationBuilders.terms(ageAgg).field(age).size(10);sourceBuilder.aggregation(aggregationBuiler);// 聚合平均年龄AvgAggregationBuilder balanceAggBuilder AggregationBuilders.avg(balanceAgg).field(age);sourceBuilder.aggregation(balanceAggBuilder);sourceBuilder.size(0); // 聚合的时候就不用显示满足条件的文档内容了searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);System.out.println(sourceBuilder);// 2.如何执行检索操作SearchResponse response restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 3.获取检索后的响应对象我们需要解析出我们关心的数据System.out.println(response);}Testvoid searchIndexResponse() throws IOException {// 1.创建一个 SearchRequest 对象SearchRequest searchRequest new SearchRequest();searchRequest.indices(bank); // 设置我们要检索的数据对应的索引库SearchSourceBuilder sourceBuilder new SearchSourceBuilder();// 查询出bank下 address 中包含 mill的记录sourceBuilder.query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery(address,mill));searchRequest.source(sourceBuilder);// System.out.println(searchRequest);// 2.如何执行检索操作SearchResponse response restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, MallElasticSearchConfiguration.COMMON_OPTIONS);// 3.获取检索后的响应对象我们需要解析出我们关心的数据// System.out.println(ElasticSearch检索的信息response);RestStatus status response.status();TimeValue took response.getTook();SearchHits hits response.getHits();float maxScore hits.getMaxScore(); // 相关性的最高分SearchHit[] hits1 hits.getHits();for (SearchHit documentFields : hits1) {/*_index : bank,_type : account,_id : 970,_score : 5.4032025*///documentFields.getIndex(),documentFields.getType(),documentFields.getId(),documentFields.getScore();String json documentFields.getSourceAsString();//System.out.println(json);// JSON字符串转换为 Object对象ObjectMapper mapper new ObjectMapper();Account account mapper.readValue(json, Account.class);System.out.println(account account);}//System.out.println(relation.toString()--- value --- status);}static class Account {private int account_number;private int balance;private String firstname;private String lastname;private int age;private String gender;private String address;private String employer;private String email;private String city;private String state;public int getAccount_number() {return account_number;}public void setAccount_number(int account_number) {this.account_number account_number;}public int getBalance() {return balance;}public void setBalance(int balance) {this.balance balance;}public String getFirstname() {return firstname;}public void setFirstname(String firstname) {this.firstname firstname;}public String getLastname() {return lastname;}public void setLastname(String lastname) {this.lastname lastname;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age age;}public String getGender() {return gender;}public void setGender(String gender) {this.gender gender;}public String getAddress() {return address;}public void setAddress(String address) {this.address address;}public String getEmployer() {return employer;}public void setEmployer(String employer) {this.employer employer;}public String getEmail() {return email;}public void setEmail(String email) {this.email email;}public String getCity() {return city;}public void setCity(String city) {this.city city;}public String getState() {return state;}public void setState(String state) {this.state state;}}
}